Change of State
Change of State: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Mixing of Liquid and Vapour at Different Temperatures, Mixing of Liquid and Solid at Different Temperatures, Latent Heat, Temperature Versus Heat Graph for Heating of Ice, and Latent Heat of Sublimation.
Important Questions on Change of State
Which of the following is not an example of sublimable substances?
Which of the following is not an example of sublimable substances?
Explain the process of sublimation.
The _____ melting point, also known as the complete melting point because temperature at given rate becomes completely clear.
The melting point(K) of mercury is 236.
The melting point ( K) of aluminium is:-
What are the common factor which is responsible for increase in melting point?
Ice melts when energy in the form of ____ is supplied
Conversion of Solid into liquid is called _____.
The amount of heat required to convert a unit mass of solid into gas is
The process in which a solid directly changes into gaseous state is called_____.
The process in which a solid directly changes into gaseous state is called evaporation.
What is Latent Heat of Sublimation.
The normal boiling point of a liquid is that temperature at which vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to:
All liquids boil at higher temperature than their normal boiling point when they contain _____ impurities.
All liquids boil at higher temperature than their normal boiling point when they contain non-volatile impurities.
What is meant by Normal Boiling Point?
Observe the following temperature Vs. time graph and fill in the blank:
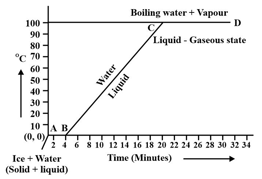
During transition of solid phase to liquid, the object absorbs _____ energy, but its temperature does not increase.
A block of ice at is slowly heated and converted to steam at . Which of the following curves represent the phenomenon qualitatively?
Two systems are in thermal equilibrium. The quantity which is common for them is
